Clay Hypoplasticity (Mašín, 2014)
Views 14,513
Clay hypoplasticity is an advanced incrementally non-linear constitutive model based on critical state soil mechanics developed specifically for simulation of fine-grained materials.
SANISAND (Dafalias and Manzari, 2004)
Views 13,212
SANISAND is an advanced elasto-plastic model based on a concept of rotational hardening incorporating the effects of fabric-dilatancy.
Sand Hypoplasticity (von Wolffersdorff, 1996)
Views 8,411
Sand hypoplastic model is an advanced incrementally non-linear constitutive model for sand, an outcome of an extensive research at Karlsruhe University in 1990's.
The PM4Sand and PM4Silt models are stress-ratio controlled, critical state compatible, bounding surface plasticity models developed for geotechnical earthquake engineering applications.
Extended Mohr–Coulomb (EMC)
Views 3,680
A simple soil model for predicting settlement of shallow foundations on sand. It incorporates a simple isotropic linear elastic component, a Mohr–Coulomb yield surface, the original Cam Clay flow rule and a simple asymptotic strain-hardening rule.
Barodesy (Kolymbas, Medicus, Schneider-Muntau, Fellin)
Views 2,542
Barodesy is a constitutive model for granular media and does not use standard notations of elasto-plasticity, e.g. yield function, flow rule or plastic potential.
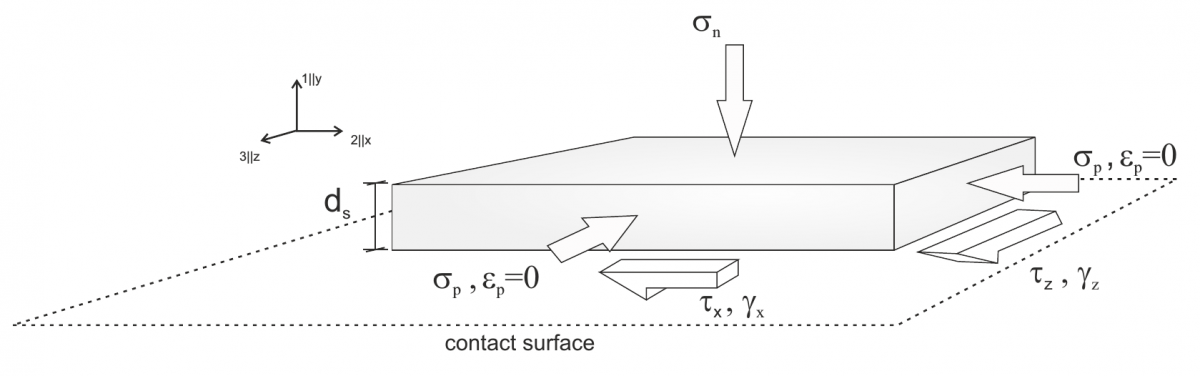
Hypoplastic Interface Model (Stutz et al., 2016)
Views 2,205
Model to represent the behaviour of interfaces based on hypoplasticity. A general approach to model interfaces using continuum constitutive models is adopted.
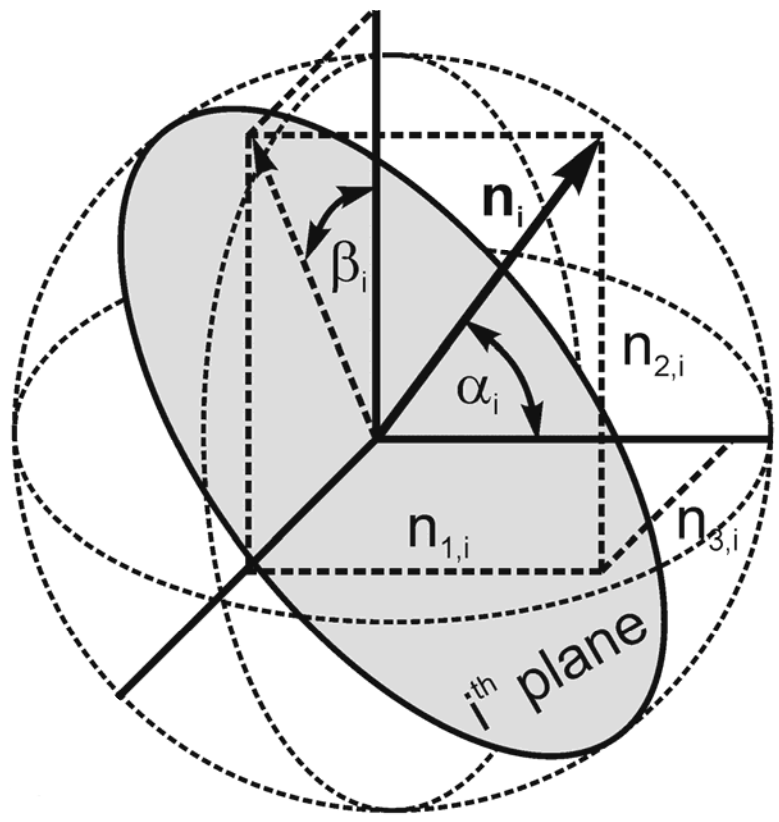
Multilaminate constitutive models are based on the concept that the material behaviour can be formulated on a number of so-called integration planes with varying orientation. In addition to other features, the model predicts anisotropic soil stiffness at small strains.
The PM4Sand and PM4Silt models are stress-ratio controlled, critical state compatible, bounding surface plasticity models developed for geotechnical earthquake engineering applications.
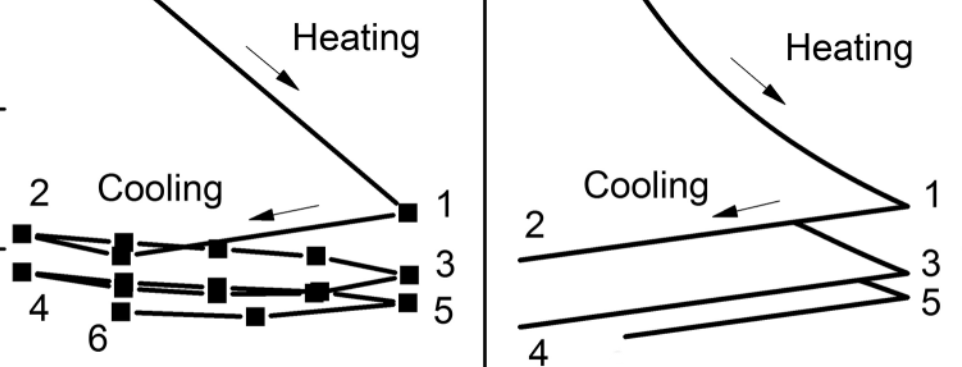
Hypoplastic Model for Thermal Cycles (Ma et al., 2017)
Views 1,328
Model to simulate the cumulative feature of volumetric contraction of fine-grained soil subjected to thermal cycles. A thermal stabilization line is introduced to control the stabilized volumetric contraction under thermal cycles.
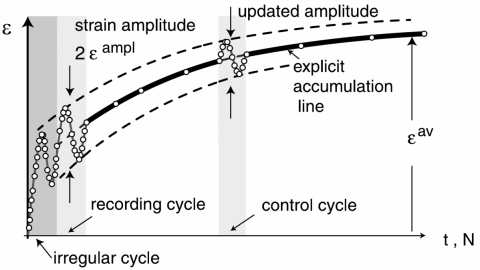
A High-Cycle Accumulation Model for Sand (Niemunis et al., 2005)
Views 888
A high-cycle explicit model for the accumulation of strain in sand due to small cyclic loading. The dependence of the accumulation rate on stress, void ratio, cyclic history and the type of loading is considered. In particular, the ovality and the polarization of the strain path during a cycle are taken into account.



Recent Comments